Study on performance of Echo MRI900 mouse body composition analyzer
First, the research background
When studying the causes of neurological, physiological, and endocrine mechanisms that cause weight gain, it is necessary to quickly obtain accurate and reproducible body components. Many obesity-related diseases are usually associated with increased body fat rather than weight, and methods for measuring body weight or BMI do not provide information on fat content and are therefore not suitable for such studies. Traditional methods for determining body fat and muscle content, such as whole body chemical composition analysis (CCA), are not only time consuming, but also require animals to be sacrificed, so animals cannot be observed continuously for long periods of time. New techniques, such as bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) and dual-energy x-ray absorption (DXA), allow repeated observations of live animals, but both require anesthesia. At the same time, the BIA method measures the body component content error of obese animals, while DXA takes a long time to detect animals (5-35 minutes). The method of measuring body composition by quantitative magnetic resonance (QMR) is superior to CCA, BIA and DXA because QMR can perform rapid body composition testing on living, unanesthetized animals, and this method does not X-ray radiation damage.
BIA can only measure total water directly, and DXA directly measures fat and non-fat content. The measurement principle of EchoMRI is that the characteristics of H-nuclear magnetic resonance in liquid and tissue are different, and the density of H atom is also different. This difference can be used to measure fat mass, muscle mass, total body water volume and free water volume. Suitable for human body and various animals.
Second, the experimental method
In this study, we compared the EchoMRI-900 (Echo Medical Systems, Houston, TX), an instrument that analyzes the body composition of mice and rats, by comparing it to the traditional CCA method. The purpose of the experiment is as follows: 1. Compare the measurement results of two measurement methods on outbred, lean and obese mice and rats; 2. Determine the results of QMR on the fat and muscle mass of animal carcasses and living bodies. Whether it is consistent; 3. Compare the accuracy of the two methods of QMR and CCA; 4. Study the effect of short-term fasting and water-free on the fat and muscle mass measured by QMR method.
Third, part of the experimental results
Body composition measurement of living animals by QMR and CCA
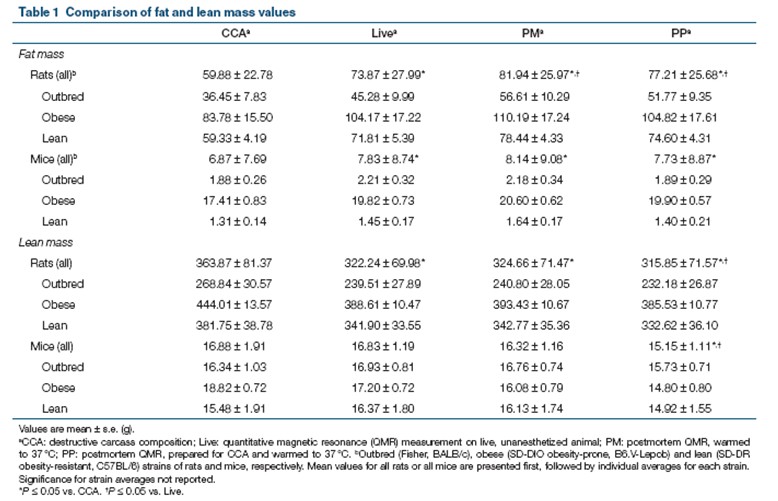
Table 1. Comparison of fat mass and muscle mass between rats and mice by two different methods of QMR and CCA
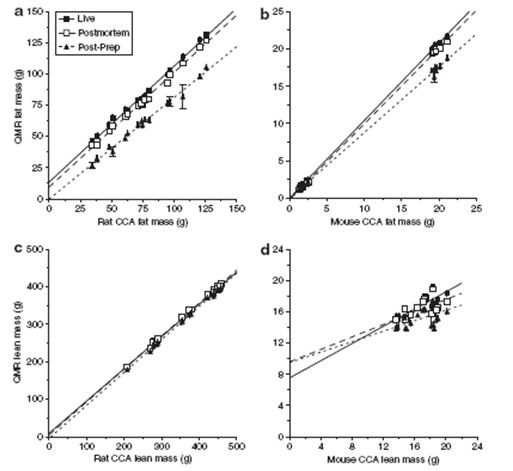
Figure 1. Determination of fat and muscle content in rats and mice by QMR and CCA methods, respectively
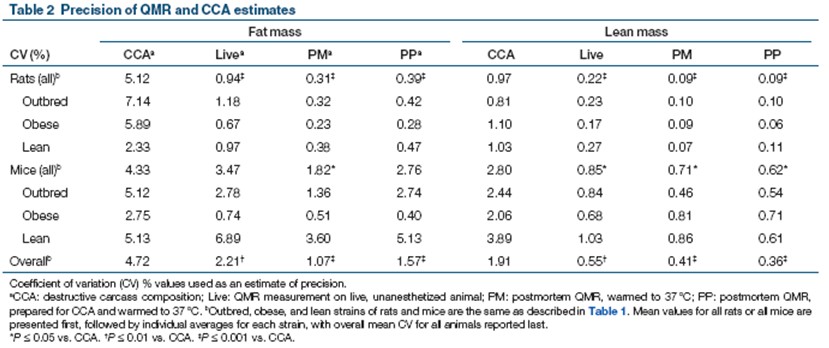
Table 2. Accuracy of values ​​measured by QMR and CCA methods
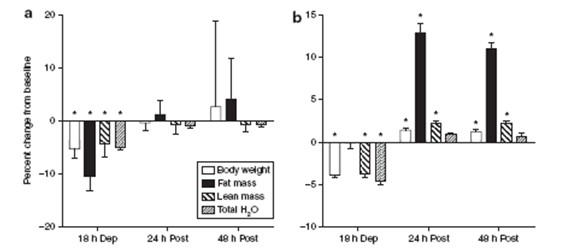
Figure 3. Effect of fasting or no water on QMR measurements.
Fourth, the conclusion
In this experiment, we used the rat and mouse combination system Echo MRI900 body composition analyzer to measure the fat and muscle content of rats and mice, and compare the results with the results obtained by the traditional CCA method. Although the results of the Echo MRI900 are not exactly the same as those of the CCA, especially the determination of the muscle content. However, a linear comparison between the two can be made by mathematical formulas. We found that the QMR system measured higher values ​​of fat and muscle mass than CCA (mean QMR CV difference vs. CCA = 2.5% and 1.4% for fat and lean mass, respectively), and Echo MRI900 was large The accuracy of the mouse and mouse measurements was the same as that of the Echo MRI100 instrument used to measure the mice alone.
Our results show that the combined QMR system measures fat and muscle mass more accurately than the CCA method. We fast or water-free rats or mice in a short period of time (less than 1 day), Echo MRI900 can measure Minor changes in body composition caused by fasting (water). In summary, the Echo MRI 900 combination system provides fast, accurate and completely non-invasive body composition measurements in rats and mice. The results can be compared to chemical analysis (CCA) and measured much faster than chemical analysis. .
From Obesity (2010) doi:10.1038/oby.2009.471
Cooling Patch(Gel series)
Surgimed Medical Supplies Co.,Ltd , https://www.surgimedcn.com