Photoacoustic imaging for detecting ovarian cancer
Key words: photoacoustic imaging ; Raman resonance absorption ; SERRS; surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy ; gold nanorods ; ovarian cancer ; Endra nexus 128
Ovarian cancer is one of the common tumors of female reproductive organs, and its incidence rate ranks third only after cervical cancer and endometrial cancer. However, due to the death of ovarian cancer, it is the first in all kinds of gynecological tumors, posing a serious threat to women's lives. Clinical data at home and abroad, if early diagnosis can be obtained, 90% of patients can survive through treatment; but if advanced, cancer cells spread to the ovary, the survival rate will be less than 30% . Because the clinical symptoms of ovarian cancer are concealed, the vast majority of patients are clinically advanced at the time of presentation. Therefore, early detection and early diagnosis are prerequisites and guarantees for improving the cure rate, prolonging the survival period and improving the quality of life.
Recently, researchers at Stanford University have used photoacoustic imaging and Raman imaging for the first time to use gold nanorods as tumor targeting markers, and observed 2008, HEY, and SKOV33 cell line ovarian tumors transplanted subcutaneously in vivo . The study found that the maximum intensity of photoacoustic signals can be observed by injecting gold nanorods into mice for 3 hours. The signal can last until two days after injection; the higher the concentration of gold nanorods, the stronger the photoacoustic signal, both of which are good. The linear relationship. Through Raman imaging, the edge of the tumor and normal tissue can also be clearly distinguished. Imaging of ovarian cancer in vivo is achieved for the first time using photoacoustic and Raman contrast agents.
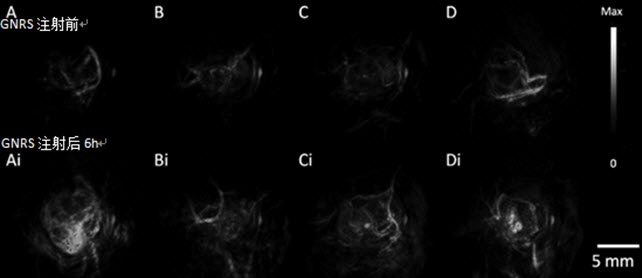
Photoacoustic imaging of MDA-435S (A, control ) 2008 (B), HEY (C), and SKOV3 (D) ovarian tumors using gold nanorods (instrument: Endra Inc. Nexus 128)
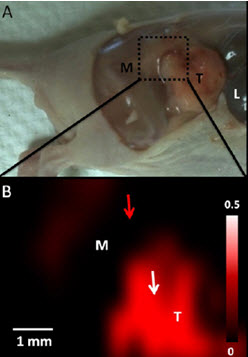
Raman imaging of ovarian cancer. M: normal tissue T: tumor (instrument: InVia, Renishaw)
Gold nanorods strongly scatter light in the near-infrared region, and the scattering background of the organism in this band is weak, so that the gold nanorods can act as near-infrared fluorescent probes that can enter and exit the optical window of human tissues, and pass through various groups. Targeting for tumor cells is obtained after modification. Gold nanorods pass through an adjustable aspect ratio, and their plasmon resonance absorption peaks produce different degrees of red shift. In this paper, three kinds of gold nanorods with aspect ratio were studied . Finally , the contrast agent with the resonance absorption peak of 750nm was used as the contrast agent for photoacoustic imaging and Raman imaging. It has a good observation effect on ovarian cancer.These findings have laid a good foundation for the potential application of gold nanorods for early detection of tumors, molecular imaging and targeted therapy. At present, the early diagnosis methods of ovarian cancer are mainly tumor markers and modern imaging examination. Imaging mainly includes CT , MRI , PET and other means. Among them, B -mode is the preferred detection tool with real-time and low cost. B -ultrasound with photoacoustic imaging is expected to provide more favorable evidence for clinical detection of tumors.
Advanced imaging technologies such as photoacoustic imaging will provide a more reliable and accurate diagnostic tool for early clinical detection of tumors.
Original summary :
†Molecular Imaging Program at Stanford (MIPS), Department of Radiology, Stanford University, 318 Campus Drive, Stanford, California 94305-5427, United States,
And ‡Bioengineering, Materials Science & Engineering, Bio-X, Stanford University, Stanford, California 94305, United States
Abstract:Improved imaging approaches are needed for ovarian cancer screening, diagnosis, staging, and resection guidance. Here, we propose a combined photoacoustic (PA)/Raman approach using gold nanorods (GNRs) as a passively targeted molecular imaging agent. GNRs with three Different aspect ratios were studied.Those with an aspect ratio of 3.5 were selected for their highest ex vivo and in vivo PA signal and used to image subcutaneous xenografts of the 2008, HEY, and SKOV3 ovarian cancer cell lines in living mice. Maximum PA signal Was observed within 3 h for all three lines tested and increased signal persisted for at least two days postadministration. There was a linear relationship (R2 = 0.95) between the PA signal and the concentration of injected molecular imaging agent with a calculated limit of detection of 0.40 nM GNRs in the 2008 cell line. The same molecular imaging agent could be used for clear visualization of the margin between tumor and normal tissue and tumor debulking After surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) imaging. Finally, we validated the imaging findings with biodistribution data and elemental analysis. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of in vivo imaging of ovarian cancer tumors with a photoacoustic and Raman Imaging agent.
Fruit and vegetable powder is the fresh fruits, vegetables through the international advanced level of freeze-drying technology and equipment, through pretreatment, quick-freezing, vacuum drying, ultraviolet sterilization, packaging and storage, and other more than 10 processes processing. Fruit and vegetable powder can be applied to almost every field of food processing, can be used to improve the nutritional composition of products, improve the color and flavor of products, etc.
Apple Cider Vinegar Powder,Blueberry Powder,Dragon Fruit Powder,Black Elderberry Powder,Wheat Barley Grass Powder,Matcha Green Tea Powder
Xi'an Gawen Biotechnology Co., Ltd , https://www.amulyn-bio.com