Summer corn needs less fertilizer at the seedling stage, and a large amount of fertilizer is required from the ear to the flowering stage, and gradually decreases thereafter.
First, the effect of fertilizer production increase
Summer corn is a crop that requires more nitrogen. Under normal circumstances, nitrogen can increase production by about 30%. However, with the increase in the amount of nitrogen fertilizer input, the supply of nutrients in the soil is unregulated, and balanced fertilization must be carried out in order to capture the high yield of corn. The application of nitrogen and phosphorus combined with summer maize increased the yield by 47%; and the combined application of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium increased the yield of summer maize by more than 60%.
Second, scientific fertilization formula
The yield of summer corn does not increase in proportion to the amount of fertilizer applied. It exceeds a certain amount, and the higher the amount of fertilizer, the lower the yield. Field experiments must be conducted to determine economically reasonable fertilizer formulations.
(1) Based on the local production formula, the fertility is divided into three levels based on the yield of non-fertilized summer maize: the yield is less than 3,750 kg for each hectare of summer maize; the yield is 3750-5250 kg; the yield is more than 5250 kg; field. Low-yielding fields need to apply 256-224 kg of pure nitrogen, 120-150 kg of phosphorus pentoxide, and 0-75 kg of potassium oxide per hectare. In the middle production field, 180-225 kg of pure nitrogen, 105-120 kg of phosphorus pentoxide and 75-105 kg of potassium oxide need to be applied per hectare. High-yielding fields need to apply 180-195 kg of pure nitrogen, 105 kg of phosphorus pentoxide, and 105-135 kg of potassium oxide per hectare.
(2) Soil testing and fertilizing formula The determination of soil nutrients determines the economic and efficient fertilizer formulation. Soil alkaline nitrogen below 50 mg kg, available phosphorus below 15 mg/kg, available potassium below 80 mg/kg for low-yielding fields; soil alkaline nitrogen for 60–110 mg/kg, available phosphorus 15–30 mg/kg , Available potassium 80-120 mg / kg for the middle field; soil alkalinity more than 110 mg / kg, available phosphorus more than 30 mg / kg, fast-acting potassium more than 120 mg / kg for high yield fields. Low-yielding fields: The target yield requires 165-200 kg of pure nitrogen, 105-120 kg of phosphorus pentoxide, and 90-120 kg of potassium nitride per hectare. In the middle field, 165-175 kg of pure nitrogen, 80-90 kg of phosphorus pentoxide, and 90 kg of potassium oxide are required for each hectare. High-yielding fields need to apply about 120 kg of pure nitrogen, 15-20 kg of phosphorus pentoxide, and 30-90 kg of potassium oxide per hectare.
Third, the appropriate period and method of fertilization
(1) Apply base fertilizer. Phosphorus and potassium fertilizers were used as base fertilizers in fertilizer formulations; 60% nitrogen fertilizer was used as base fertilizer. For the soil with poor water retention and fertility retention performance, the top dressing is mainly used. The basal fertilizer should be evenly spread on the surface, and plowed into the 20-cm deep soil.
(2) Qiao applied fertilizer. From the fertilization formula, 15-22.5 kg of pure nitrogen, 45 kg of phosphorus pentoxide, and 15-22.5 kg of potassium oxide were used as seed fertilizers. It is forbidden to contact with the seeds and lay the foundation for training strong seedlings.
(3) Use top dressing. Topdressing is mainly nitrogenous fertilizer. There is no phosphorus or potassium fertilizer in the base fertilizer. Top dressing is divided into seedling fertilizer, jointing fertilizer and panicle fertilizer. Miao Fei should be light to ensure Miao Qi, Miao Zhuang. Jointing fertilizer refers to top dressing from the jointing of corn to the small bellmouth period, which generally accounts for 40% of top dressing. The attacking fertilizer refers to the fertilizer applied by corn during the trumpet season, and generally accounts for 60% of the topdressing fertilizer.
The topdressing method can be applied, or it can be applied in a depth of 15cm or so.
(4) Use top dressing outside the roots. Extra-root fertilizer is an auxiliary emergency measure. This method is often used when there is a lack of symptoms or if there is a decline in root function. With 1% urea solution or 0.08%-0.1% potassium dihydrogen phosphate solution, the foliar spray was performed at 4 o'clock on sunny days.
Fourth, rational application of fertilizer
The amount of zinc, boron, and manganese base fertilizers used in the fields lacking trace elements was 10 kg, 7 kg, and 20 kg per hectare. Apply a suitable amount of fine soil when applied, evenly spread on the surface, plow into the soil. When used as a fertilizer, 0.01%-0.05% solution can be used for soaking for 12-24 hours. After drying, it can be sowed. 0.1%-0.2% of the solution can also be used for extra-root fertilizer, 900 kg/ha, sprayed twice, the time interval of about 15 days.
L-Glutamine Basic Information
Description References
Product Name: L-Glutamine
CAS: 56-85-9
MF: C5H10N2O3
MW: 146.14
EINECS: 200-292-1
Mol File: 56-85-9.mol
L-Glutamine Structure
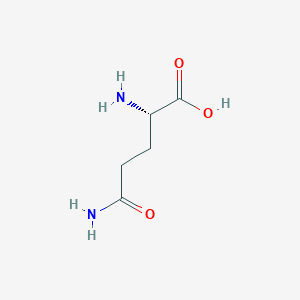
Melting point 185 °C (dec.)(lit.)
alpha 32.25 º (c=10, 2 N HCl)
Boiling point 265.74°C (rough estimate)
density 1.47 g/cm3 (20℃)
refractive index 6.8 ° (C=4, H2O)
Fp 185°C
storage temp. −20°C
solubility H2O: 25 mg/mL
pka 2.17(at 25℃)
form solution
color White
PH 5.0-6.0 (25℃, 0.1M in H2O)
Water Solubility Soluble in water, dimethyl sulfoxide and ethanol. Insoluble in methanol, ether, benzene, acetone, ethyl acetate and chloroform.
Decomposition 185 ºC
l-glutamine,l-glutamine uses,uses for l-glutamine,l-glutamine benefits,l-glutamine powder,l-glutamine in food
ShanDong YingLang Chemical Co.,LTD , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com