Scientific name Euptote chinensis Leech Lepidoptera, with moth family. Alias ​​black caterpillar. Distribution Hubei, Hunan, Guangxi, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan.
The host Paulownia, pomegranate, peach, apple and so on.
The larvae harm the characteristics of the host's leaves. The light leaves the host's leaves bite into many holes and nicks, and can seriously eat the leaves or bite the tender branches of the bark. Affecting the growth and development and flowering results, the production of plants for administration and fruit trees caused considerable losses.
Morphological characteristics Adult moth female body length 22-28mm, wingspan 67-88mm. All gold. Yellow antennae, filamentous. Chest and fin base densely grow scales. Wide wings, irregular reddish long-spots on the fins of the forewings, grayish white scales on the surface of the long spots, 2 round spots under the long spots, a small spot on the posterior horns, and 5 or 6 on the wing surface. The red wavy lines are thick and obvious in the frontal area. There are 5 or 6 spots in the middle of the hind wings, and they are arranged neatly. There are 3 large spots on the outside of the spots. The top corner area is one size and each is close to each other. There are four wavy lines in the trailing edge area, which are thick and obvious. The male body is 20-27mm long and its wingspan is 58-82mm. Body fins golden yellow. Antennae yellow-brown, feathery, longer plumes. Chest with golden scales, belly brown. The front wings of the forewings are tan-brown, with a large triangular-red spot in the vertex area; the silvery-gray dots are not obvious in the lower half of the large spot; the small spots are 7-8 long in the sub-marginal spots, and there is a larger one in the inner rear corner. Spots, the entire wing surface has 5 intermittent wavy lines; the front edge area is thick and obvious. The fins of the hind wings are wavy, with 2 rows of small spots on the inside, and 4 intermittent wavy vertical bands in the inner half of the wings. The oval is spherical and the contact is slightly flat. Diameter 1.2-1.3mm. Light yellow, shiny, opaque, with a black spot on the top of the egg near hatching. The last instar larvae are 46-71mm in length. Cylindrical. The ventral surface is slightly flat and the whole body is dark brown. There was a convex-shaped black spot in the middle of the back of each abdominal segment, and eight black spots on the back of the abdomen. The head shell is dark brown. On the back and sides of the body there are many secondary thorns and long bundles of hairy hair. The thoracodorsal and tail segments are slightly longer and extend forward and backward, respectively. Banded hairy brown, brown and gray and white, but often mixed together. Three pairs of chest feet, l pairs of tail. The ventral toe hooks are bi-order semi-rings with 80 to 92 toes per foot. It is spindle-shaped, blunt at the tip, slightly pointed at the end, and has small spines. Length 21-28mm, thick 8-9mm. Dark brown, shiny. There are thin oysters outside the oysters, long oval, 1/3 larger than the pod. Brown-brown or brown-gray, made of silk fabric, gauze-like, thin and soft, breathable. It often sticks together with fallen leaves and grass clippings.
Habits of life 1 generation in Sichuan, with quail winter, overwintering period of up to 7-8 months. In early July, adults were seen. From late July to early August, adult emergence emerged. In the middle and late August, a small number of adults could be caught. The adult emergence period was very long, and it spanned 2-3 months before and after. Adults have strong phototaxis. After the adult has emerged, it will stop at the weeds near the overwintering area or under the canopy, and will start activities, fly and mating after dusk. Feathers are mostly in the evening, mating on the second day, mating, and spawning on the evening of the mating or the night of the second day. The male dies after several matings, and the female dies after the eggs are laid. Adults live 7-10 days. Female moths lay their eggs on the back or twigs of the host's leaves. The eggs are concentrated into pieces. One is irregularly next to the other and only one is layered. It is often composed of hundreds of grains. 115-187 eggs per female, egg period 8-12 days, and some up to more than half a month. Most larvae are 6 years old. The newly hatched larvae are drilled from the top of the egg and can eat or eat most of the egg shells within half a day to 1 day. After larvae are hatched, they colonize in groups on the back of the leaves when they are 1-2 years old. The young larvae have the habit of pendulous drooping and spreading with the wind after being frightened. The larvae move forward following the larva action. After 3rd instar, the food intake of larvae increased greatly. During the daytime, the nests were clustered on the upper part of the trunk and the shading, bending, dents, and tree holes of the large branches. There were at least one or twenty heads, more than one hundred heads, and more than one thousand at dusk. While climbing to the branches and leaves of the tree crowns to feed on the leaves, they began to move downwards in groups before the dawn, and the actions were neat and they were connected end to end. As the worm age increases, the height of the inhabitant descends to the base of the trunk, and the larvae of one tree often gather in one place. In the event of extreme food shortages, there are cases of transgenic plants. The host leaves are often eaten as missing holes or eaten away, leaving only leaves and veins. In severe cases, the young shoots and bark are also eaten. After the third molting, the "convex" shaped dark spots on the back of the abdominal segment were clearly visible. Most of the larvae have been molted 5 times, some molting 6 times, and within 3 or 4 days before and after each molting period, the larvae's activity and feed intake have been greatly reduced. The larval period lasts for 80-95 days. The larvae are concentrated in the September-October months of fruit picking in fruit trees such as pomegranates, peaches, pears, and apples. The damage of the Chinese golden strip moth after fruit harvesting is often overlooked, and it is also mistakenly thought that this is the result of early defoliation. From mid-late October to early November, the mature larvae are cockroached and littered in the same way as the prefabricated skin, tree-holes, or deciduous trees, rolling leaves, dead branches, grasses, stone seams, and soil 7. The larvae reduce their pre-tanning activity, they do not feed, they defecate a lot, the body is shortened and thickened, and they are stored in the debris in the area where they are made. The larvae can be made into larvae in about one day. All the long hair has fallen off. On the 2nd and 3rd days, the phlegm is removed. Chinese golden moths occur in Hunan about one month earlier than in Sichuan.
Prevention methods (1) clean the pastoral. In the winter and spring season, the dead branches, fallen leaves, leaf curls, cracks, weeds, stones, etc. in the garden will be removed, the overwintering mites will be eliminated, and the source of insects will be reduced in the coming year. (2) Light trapping. Adults have strong phototaxis, from July to August, combined with the control of other pests, installation of black light or other incandescent lamp can trap some adults. (3) Protect and use natural enemies. This parasite has parasitoid parasitism during the egg and pupal stages, and has larval predation during the larval period. It should be well protected and utilized natural enemies throughout the prevention and control process. (4) Manually remove eggs. The eggs of the Chinese golden moth are concentrated on the leaves and the newly hatched larvae are clustered. When the adults lay eggs or when the larvae are newly hatched, the leaves with eggs or larvae are manually removed in time. (5) Clear larvae. From September to October, the third instar larvae often migrate downwards and clustered on the base or large branches of the trunk during the daytime. It is easy to be found. After discovery, it is often fired. It can burn dozens of heads to hundreds of heads at a time. Pay attention to safety; it can also be used to scrape off larvae and step on to death. It is also possible to bury the larvae in soil pits. The covered soil should be compacted. (6) Chemical control The larvae of all ages are mostly clustered on branches or branches. Except for manual removal and killing, 90% crystals of trichlorfon 1000-1200 times or 50% of chlorpyrifos EC 1200 are also available. - 1500 times solution, 50% phoxim EC 1000-l500x solution, 50% dichlorvos EC 1000x solution, and 50% Malathion 1000-1500x solution can all receive good control effect. The time is best for daytime larvae to gather the base of the trunk.
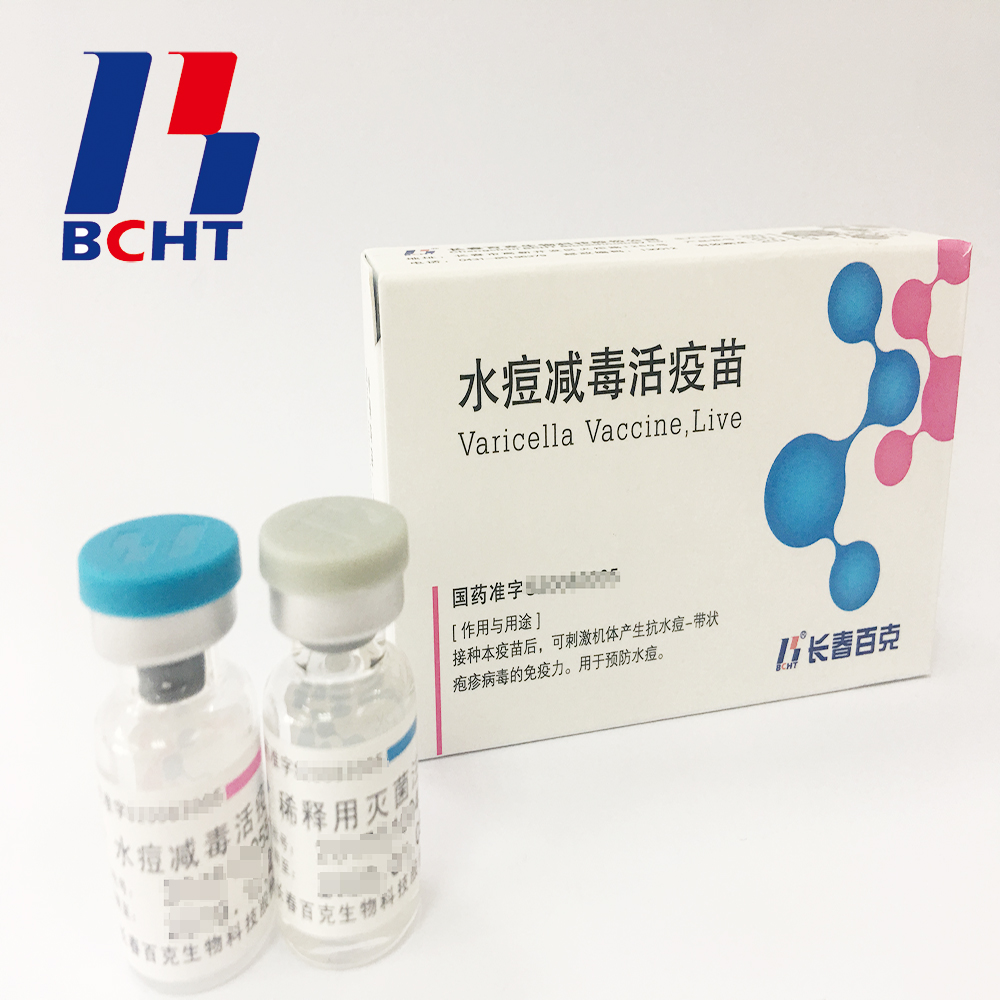
Bulk of varicella vaccine,semi-Finished Products.It has good safety with low ratio in adverse reaction. And it has been exported to Bangladesh.
In 2008, BCHT successfully launched its product Varicella Vaccine, Live in China. In the following years, BCHT continuously committed to improving the product and led in 2010 removal of gelatin from adjuvant and extended the vaccine shelf-life up to 36 months which is the longest one in the world in 2011. And it has the following qualities.
Rabies Vaccine,Freeze-Dried Rabies Vaccine,Mild Rabies Vaccine,Stable Rabies Vaccine For Human Use
Changchun BCHT Biotechnology Co.,Ltd , https://www.ccbcht.net