Detection and identification of non-target unknown pollutants during time-lapse screening by time-of-flight mass spectrometry
Purpose <br>The successful identification of a non-target unknown contaminant found in natural river water during the extensive pesticide screening of environmental water sources using time-of-flight mass spectrometry.
background
TOF screening is often used for target screening; in this case, a comprehensive database is used to target key target compounds during the screening process. Pesticide contamination screening is one of the most important analyses when analyzing environmental water sources. However, other contaminant species such as veterinary drugs or human drugs and their metabolites may also exist at sub-micro levels similar to pesticides and can cause equivalent damage to aquatic ecosystems. Once a non-target compound is discovered, it needs to be identified and identified. TOF instruments must be sensitive and accurate enough to ensure that unknown compounds are correctly detected and identified while maintaining the quality accuracy of very low concentration components. Accurate mass data on low-energy precursor ions and MSE high-energy fragment ions, as well as narrower chromatographic extraction windows, provide greater confidence in the identification of non-target species.
solution
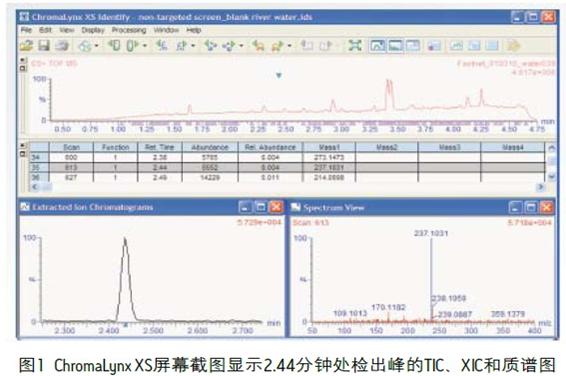
Waters® XevoTM G2 QTof, along with ACQUITY UPLC® and ChromaLynxTMXS data processing software, is used to quickly screen natural river water extracted from Oasis® HLB columns. The program uses a UPLC® universal screening gradient with a total run time of five minutes. The mobile phase used was a 10 mM aqueous solution of ammonium acetate and a 10 mM solution of ammonium acetate in methanol. A blank matrix of river water was screened to investigate any background contamination that may exist. After deconvolution by ChromaLynx XS software, a distinct peak of ion m/z 237.1031 was found at 2.44 minutes, as shown in Figure 1.
background
TOF screening is often used for target screening; in this case, a comprehensive database is used to target key target compounds during the screening process. Pesticide contamination screening is one of the most important analyses when analyzing environmental water sources. However, other contaminant species such as veterinary drugs or human drugs and their metabolites may also exist at sub-micro levels similar to pesticides and can cause equivalent damage to aquatic ecosystems. Once a non-target compound is discovered, it needs to be identified and identified. TOF instruments must be sensitive and accurate enough to ensure that unknown compounds are correctly detected and identified while maintaining the quality accuracy of very low concentration components. Accurate mass data on low-energy precursor ions and MSE high-energy fragment ions, as well as narrower chromatographic extraction windows, provide greater confidence in the identification of non-target species.
solution
Waters® XevoTM G2 QTof, along with ACQUITY UPLC® and ChromaLynxTMXS data processing software, is used to quickly screen natural river water extracted from Oasis® HLB columns. The program uses a UPLC® universal screening gradient with a total run time of five minutes. The mobile phase used was a 10 mM aqueous solution of ammonium acetate and a 10 mM solution of ammonium acetate in methanol. A blank matrix of river water was screened to investigate any background contamination that may exist. After deconvolution by ChromaLynx XS software, a distinct peak of ion m/z 237.1031 was found at 2.44 minutes, as shown in Figure 1.
The accurate and reproducible accurate mass data collected by the Xevo G2 QTof provides analysts with a solution for non-target contaminant screening and research with high confidence.
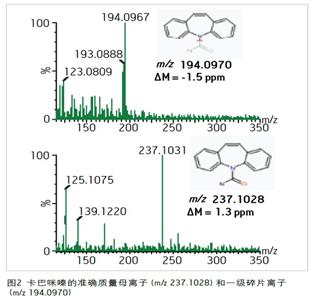
When this accurate mass ion is analyzed using the elemental composition tool in the MassLynxTM application management system, the most probable suggested formula with a maximum mass tolerance of 2.0 ppm is C15H13N2O, and this formula is selected by using i-FITTM. Best fit. This formula matches a human protonated kabatazine with an anticonvulsant and mood stabilizing drug. The low-energy mass spectrometry and MSE high-energy mass spectra collected at 2.44 minutes were then processed using the MassFragmentTM tool and matched to the parent molecule of the carbamazepine and its primary fragment ions, as shown in Figure 2.
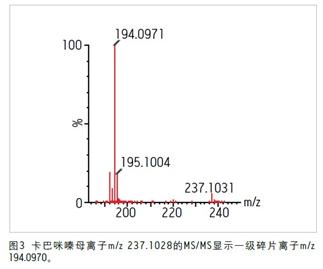
Finally, it was clearly confirmed by comparison with a solvent standard solution of pure carbamazepine. A comparison of the solvent standard data shown in Figure 3 with the non-target contaminant data clearly demonstrates that this unintended compound is carbamazepine.
Summary <br>A complete set of processes, extracted by Oasis HLB SPE, rapidly separated by ACQUITY UPLC and tested by Xevo G2 Qtof, and processed by ChromaLynx MS software, can be successfully used for natural river water screening. Detection and identification of unintended contaminants, the drug molecule, carbamazepine, was achieved using a non-target screening method. Accurate and reproducible accurate mass data acquired by the Xevo G2 QTof enables a clear assignment of parent and fragment ion structures. This approach provides analysts with a screening and research solution for non-target compounds with high confidence in the end result.
Medical Products,Medical Consumables,Medical Furniture,Medical Instruments
jiangyin chenyi medical technology co.,ltd , https://www.chenyimed.com