The study found that endogenous cholesterol ester oxidation products affect the new mechanism of cholesterol levels
December 18, 2018 Source: Chinese Academy of Sciences
Window._bd_share_config={ "common":{ "bdSnsKey":{ },"bdText":"","bdMini":"2","bdMiniList":false,"bdPic":"","bdStyle":" 0","bdSize":"16"},"share":{ }};with(document)0[(getElementsByTagName('head')[0]||body).appendChild(createElement('script')) .src='http://bdimg.share.baidu.com/static/api/js/share.js?v=89860593.js?cdnversion='+~(-new Date()/36e5)];On December 12th, the international academic journal Redox Biology published the latest research results of "Endogenous cholesterol ester hydroperoxides modulate cholesterol levels and inhibit cholesterol uptake in hepatocytes and macrophages" by the research team of Yin Huiyong, Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The study used a targeted lipidomics approach to systematically analyze various oxidized products derived from cholesterol esters in plasma of cardiovascular patients at different stages, and found that different types of cardiovascular diseases, Oxidized cholesterol ester (oxCEs) The levels are significantly different and are significantly elevated in patients with myocardial infarction. Then, a major peroxidation product (cholesteryl-13(cis,trans)-hydroperoxy-octadecadienoate, ch-13(c,t)-HpODE) is obtained by chemical synthesis, and the oxidation product pair is further explored in vitro and in vivo. The effect of cholesterol levels, while initially revealing a new mechanism of cholesterol ester peroxide affecting cholesterol levels.
Cardiovascular disease is one of the diseases with the highest morbidity and mortality. Cholesterol metabolism disorder is one of the important causes of cardiovascular disease. Previous studies have shown that Oxidized Low Density Lipoprotein (oxLDL) plays an important role in atherosclerosis, but little is known about its intrinsic component, cholesteryl ester. In recent years, studies have shown the presence of oxCEs in atherosclerotic plaques, but due to the variety and structural complexity of oxCEs, both the analysis of their clinical samples and the study of biological activity are extremely challenging.
Under the guidance of researcher Yin Huiyong, Ph.D. student Guo Yiyuan used target lipidomics to analyze normal control (Cons), coronary heart disease (CHD), and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease (CHD+Cerebrovascular disease). , CHD+CBD) and plasma samples from the myocardial infarction group (Myocardial infraction, MI). The results showed that the cholesteryl ester levels were significantly different at different stages of the disease and increased significantly in the MI group. A major endogenous oxCE was subsequently chemically synthesized and purified to study the effects of such endogenous metabolites on cholesterol metabolism. In vivo experiments showed that ch-13(c,t)-HpODE can reduce the cholesterol content of liver and peritoneal macrophages and increase plasma cholesterol levels. In vitro experiments revealed that ch-13(c,t)-HpODE can inhibit the cholesterol uptake of macrophages by activating the LXRα-IDOL-LDLR pathway; at the same time, the liver caused by ch-13(c,t)-HpODE The reduction in cellular cholesterol intake is also dependent on LDLR and LXRα.
The research was supported by Zheng Lemin, a professor at Peking University School of Medicine, Tiantan Hospital of Capital Medical University, Song Baoliang, a professor at Wuhan University, and He Ben, a professor at Shanghai Renji Hospital. He also received support from the Ministry of Science and Technology, the National Natural Science Foundation, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences. .
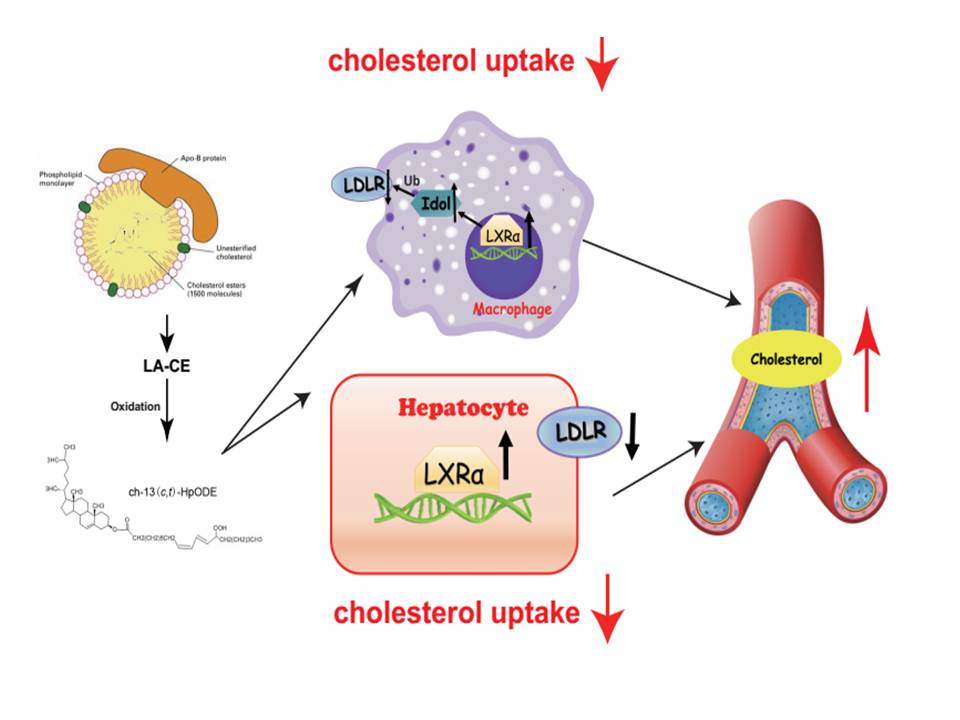
Figure: Effect of endogenous cholesterol ester peroxidation on cholesterol levels
Xi'an Healthway Biotech Co.,Ltd , https://www.xianhealthway.com