The two most common swine diseases in autumn and winter are pig haemophilus and porcine infectious pleuropneumonia. The mortality caused by these two kinds of swine diseases is particularly high, and every time the farmers are unable to say anything, then Are you ready to be greeted and prevented?
First, Haemophilus parasuis (HPS)
Serotype
The prevalence of HPS in China is mainly type 4, type 5 and type 13, followed by serum type 14 and type 12, but there are certain differences between different regions. (2016)
The virulence of different serotypes of Haemophilus parasuis is different:
High virulence: causing acute death
Serotype 1, 5, 10, 12, 13, 14
Moderate virulence: serositis and arthritis
Serotypes 2, 4, 8, 15
Low virulence: no clinical symptoms
Serotype: 3, 6, 7, 9, 11
2. Epidemiological characteristics
Prone to occur
Mainly 5 weeks old - 8 weeks old pigs, because the protective effect of maternal antibodies decreased;
Piglets in the delivery room have significant lung adhesions due to sow infection;
After secondary to other diseases.
The fattening stage rarely occurs;
The time of infection is related to the disappearance of maternal antibodies and the loss of passive protection.
3, HPS main symptoms and lesions
The most acute type has no obvious symptoms and suddenly dies;
Acute type usually occurs in pigs with good sensation and good condition. The fever of the sick pig reaches 40.5-42 °C, difficulty in breathing, decreased appetite, subcutaneous edema of the eyelid, purulent secretion in the nasal cavity, inflammation in some joints, and 2-5 days after onset. death;
Chronic type is more common in nursery pigs, loss of appetite, elevated body temperature, cough, breathing, growth, and death until exhaustion.
After the acute infection may leave sequelae, that is, sow abortion, boar chronic clam;
Serous and purulent fibrin exudate.
Joint swelling, lameness, trembling, or ataxia, lying sideways or swimming
Infected with high-toxic bacteria, fever, anorexia, asthma, cough, pain
Anorexia, cough, body lengthening, limb weakness, messy hair
Increased pericardial fluid, turbidity, a large amount of gray-white cellulose-like substance attached to the epicardium
Pulmonary congestion, edema, inflammation, and a fibrous floating membrane on the surface
Advanced suppurative pericarditis and pleuropneumonia (with secondary infection)
Arthritis, swelling of the joint capsule contains a lot of clear / turbid fluid (especially the posterior ankle joint)
4, prevention and control
(1) Pig house design and pig raising process
Ventilation and density of pig houses: At present, the general size and weight of the pigs are increased, such as 120-130kg, whether the original pig house space is sufficient;
Reasonable feeding management: use powder and dust in the pig house to increase the risk of respiratory tract;
Monitoring the types of microorganisms in the environment: the application of air samplers;
Reduce the number of mixed groups.
(2) Feeding and management: ventilation and reduction of mixed groups.
(3) Drug prevention: Mix the rice with a test mixture for one week during weaning.
(4) Immunization prevention: rational selection of vaccine and immunization procedures (domestic dominant serotypes are serum 4 and 5).
(5) Focus on synergistic prevention and control with porcine circovirus disease: In the stage of nursery pigs, these two diseases often occur in combination.
(6) Even in the northern region, it is necessary to pay attention to the prevention and control of the disease during the nursery period.
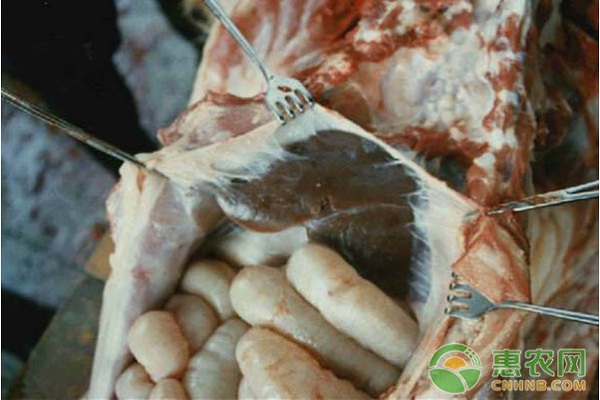

Second, porcine infectious pleuropneumonia (APP)
1, the symptoms of the disease
The most acute type: sudden onset, the body temperature of the sick pig reached 41.5 ° C or above, died within 24-26 hours, the mortality rate was as high as 80-100%, and sometimes no symptoms suddenly died;
Acute type: fever, painful cough, difficulty breathing, obvious bleeding in the nose, usually 2-4 days after the onset of illness;
Chronic: Do not love activities, varying degrees of cough, loss of appetite, slow growth, and reduced feed returns.
Bloody foam flows out of the mouth and nostrils
Minhang and dog sit
The skin of the ears, nose and limbs is blue-violet
2, the main lesions
Acute type: pulmonary congestion and hemorrhage, the trachea is filled with mucus;
Chronic type: lung adhesions, abscesses, and other organs without gross lesions.
Fibrous exudate on the surface of the lung, which adheres to the diaphragm
Inter-leaf edema, the area of ​​the bronchi filled with foam pneumonia appears brownish black
Emphysema hemorrhage, surface cellulose
Alveolar hyperemia (HE staining)
3. Prevention and control measures
(1) Pig house design and pig raising process
Ventilation and density of pig houses: At present, the general size and weight of the pigs are increased, such as 120-130kg, whether the original pig house space is sufficient;
Reasonable feeding management: use powder and dust in the pig house to increase the risk of respiratory tract;
Monitoring the types of microorganisms in the environment: the application of air samplers;
Reduce the number of mixed groups.
(2) Immunization
Vaccine selection: multivalent vaccine (consistent with epidemic serotypes) or subunit vaccine. Calculate the input-output ratio (survival rate, feed-to-meat ratio, other drug expenses, labor costs, farm farm reputation, etc.);
Immunization time: Most are 70 days old, but it is recommended to prevent it in advance according to the law of infection.
(3) drug treatment
Individual treatment with intramuscular injection of sensitive drugs often does not work well; group emergency treatment is by means of whole group administration, by means of drinking water or mixing. Pay attention to the occurrence of mixed infection with blue ear disease.
Precautions for administration:
Select sensitive drugs targeted in the lungs: tilmicosin, florfenicol, mono (da) halfloxacin; reasonable time and method of administration: determined according to the investigation of infection time.
It is recommended to eliminate individuals with poor treatment and reduce the source of infection.
Tetanus Shot,varicella vaccine, Live,Hepatitis B Injection,Hep B Vaccine
FOSHAN PHARMA CO., LTD. , https://www.fs-pharma.com