Release date: 2018-03-26
Today, a heavyweight study was published in the journal Science: the team from the Salk Institute found that mice lacking maternal love have a marked change in their genomes, and that this change is concentrated in the hippocampus that affects emotions and memories. . This finding supports the notion that "childhood's environment affects human brain development."

Image source: CC0 License, Pexels
what? Significant changes in the genome of animals after birth? Professor Rusty Gage, the director of the Salk Institute's transition, gave the affirmative answer: "The textbook says that DNA is stable, it makes us. But in reality, DNA is much more dynamic. You Some genes in the cell can replicate themselves and move around. In other words, your DNA does change to some extent."
Professor Rusty Gage, Corresponding Author of this study (Source: Salk Institute)
This phenomenon is especially common in the brain. More than a decade ago, scientists discovered that there were tiny differences in DNA sequences between neurons in the brain, partly because of "jumping genes"—these DNA sequences can travel from one locus to another. , bringing diversity to the genetic information of neurons. Professor Gage is an expert in this field. In 2005, his team discovered that a jumping gene called L1 could "jump and jump" in developing nerve cells, causing an effect.
Is this a spontaneous phenomenon of randomness, or will it be affected by the outside world? To answer this question, the researchers decided to take into account a major environmental factor in early life, maternal love. In the experiment, newborn mice first spent 2 weeks with their mothers, allowing the researchers to quantify the mother's convulsions and combing behavior. Subsequently, the mice were divided into two groups, one with more sputum and combing behavior and the other with fewer. The study found an interesting phenomenon: in mice with less attention from the mother, in the hippocampal neurons that affect emotion and memory, the copy number of the L1 gene is significantly increased, and the genetic diversity of brain neurons is therefore also more Diverse.

A mother who does not care (left) will have a genetic impact on future generations (Source: Science)
The researchers ruled out the effects of genetics alone: ​​they compared the L1 copy number of mothers and offspring, and found that this phenomenon is not simply genetic. In addition, they also analyzed tissues from the frontal cortex and heart of the offspring and found no similar changes in the copy number of L1. This further indicates that these changes are caused by the acquired environment.
Perhaps because the results were too subversive, the cautious researchers did another experiment to confirm their findings: they let the mice lacking maternal love raise the offspring of the motherly loved mice, and let those Mice with maternal love are raised to support offspring born from maternal mice. The study again showed that the L1 copy number in the hippocampus is only related to the maternal love obtained after the birth of the mouse, and has nothing to do with their biological mother.
From a mechanistic point of view, mice lacking maternal love have a significantly reduced methylation level of the L1 gene, which may increase their ability to self-replicate and jump. There were no significant changes in methylation levels on other known hopping genes. Researchers have speculated that the less care a mother has for her offspring, the greater the pressure on the mice, which specifically affects the methylation of the L1 gene, allowing them to replicate and frequently hop in hippocampal neuronal cells.
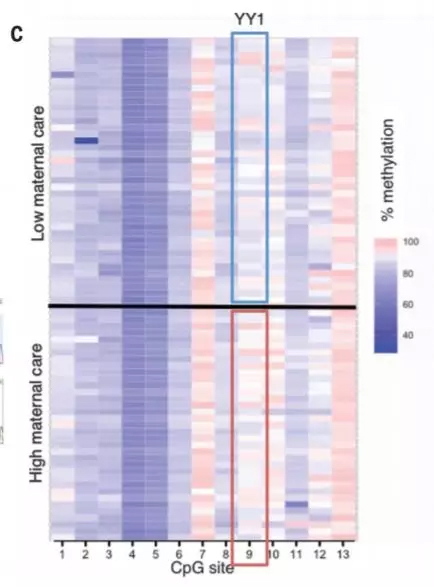
How much maternal love affects the methylation level of offspring genes (Source: Science)
“Some previous studies have shown that children who are not sufficiently cared for will show differences in the methylation of DNA. The results of this study are consistent,†Professor Gage added. “If we understand the mechanism, we can develop The strategy of intervention."
Regrettably, we don't know how this change will affect the behavior of animals. The researchers also plan to clarify this issue in the future, and hope that the new findings will let us understand whether the psychological trauma of childhood will Bring diseases such as depression or schizophrenia. While waiting for the researchers to make new achievements, if we have new mothers around us, please don't forget to remind them to care more about their babies.
Source: Academic Jingwei
Fine chemical industry is one of the most dynamic emerging fields in the chemical industry today, and it is an important part of new materials. Fine chemical products have many types, high added value, wide application and high degree of industrial correlation, which directly serve many industries of the national economy and various fields of high-tech industries. Vigorously developing Fine Chemicals has become a strategic focus for countries around the world to adjust the chemical industry structure, enhance the industrial level of a chemical industry and expand economic benefits. The state will issue relevant policies in a timely manner to build a new technology innovation organization that combines production, education and research - the National Fine Chemical Industry Technology Innovation Strategic Alliance, in order to promote the optimization and upgrading of the national fine chemical industry structure and enhance the overall competitiveness of the industry. The rate of fine chemical industry (the ratio of fine chemical output value to total chemical output value) has become an important indicator to measure the development of a country or region's chemical industry and the level of chemical technology.
Oled Materials,4-Nitrodibenzofuran,Cas 226-36-8
Shijiazhuang Dingmin pharmaceutical Sciences Co.,Ltd , https://www.dingminpharma.com